The LAB Lab
We study the relationship between the neurobiology of language, inner speech, and consciousness.
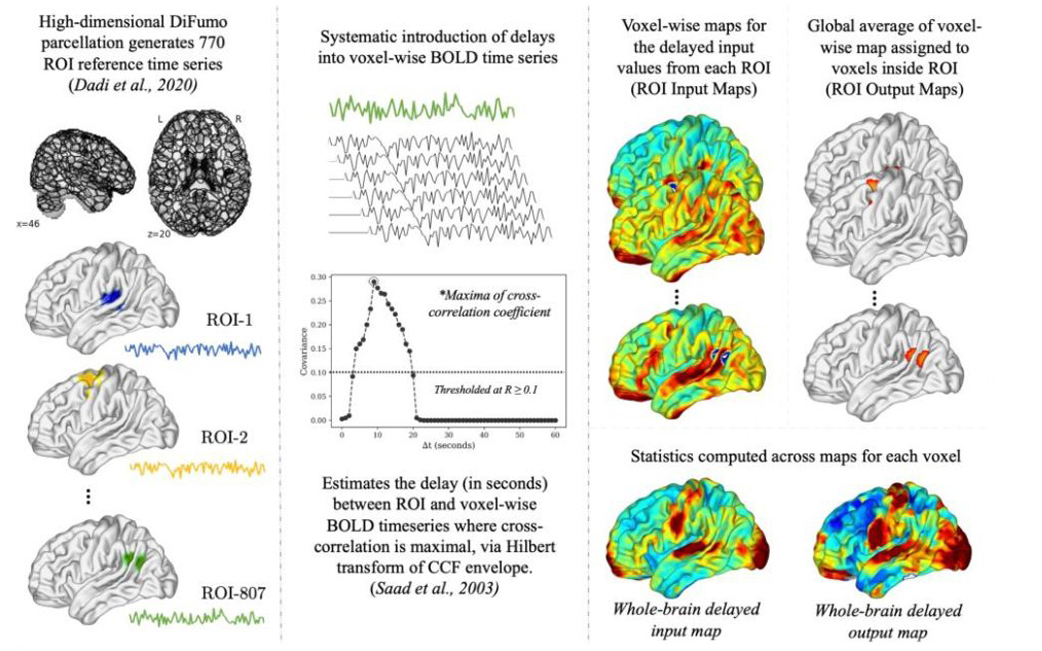
The overarching goal of the LAB Lab is to understand the the neurobiology of language, inner speech, and consciousness and their relationship to mental health and wellbeing. To achieve this aim, the LAB Lab Team uses methods and tools like naturalistic or movie-fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging), mobile phone based experience sampling and tracking, and psychedelic drugs like DMT (N,N-Dimethyltryptamine). In the spirit of open and replicable science, we do large studies and make our code and data publicly available (e.g., see our ‘Naturalistic Neuroimaging Database‘ or NNDb).
For details, see our Publications and more recent Presentations and Talks
Recent things pertaining to language, consciousness, and psychedelics
- Introductory Lecture: Consciousness, Language, Psychedelics, and the Brain
- Foundational Article: A voice without a mouth no more: The neurobiology of language and consciousness
- Meta-Analysis: The neurobiology of language mediates alterations in conscious experience induced by psychedelic drugs
- Research Group: ‘Understanding Neuroplasticity Induced by Tryptamines’ or UNITy Project
 Close
Close